Table of Contents
Target Namespace
None
Element and Attribute Namespaces
Global element and attribute declarations belong to this schema's target namespace.
By default, local element declarations belong to this schema's target namespace.
By default, local attribute declarations have no namespace.
Declared Namespaces
Prefix
Namespace
xml
http://www.w3.org/XML/1998/namespace
xsd
http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema
xsi
http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance
hl7
urn:hl7-org:v3
xlink
http://www.w3.org/TR/WD-xlink
gsd
http://aurora.regenstrief.org/GenericXMLSchema
sch
http://www.ascc.net/xml/schematron
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:schema
elementFormDefault ="
qualified ">
...
</
xsd:schema >
Complex Type: AD
Super-types:
ANY
< AD (by extension)
Sub-types:
None
Name
AD
Abstract
no
Documentation
Mailing and home or office addresses. A sequence of address parts,
such as street or post office Box, city, postal code, country, etc.
Application Data
XML Instance Representation
<...
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
use="
set_cs_PostalAddressUse
[0..1]
? "
isNotOrdered="
bl
[0..1]
? " >
<!-- Mixed content -->
Start Choice
[0..*]
<delimiter
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
representation="TXT
[0..1] "
mediaType="text/plain
[0..1] "
language="
cs
[0..1] "
partType="DEL
[0..1] " />
[1]
<country
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
representation="TXT
[0..1] "
mediaType="text/plain
[0..1] "
language="
cs
[0..1] "
partType="CNT
[0..1] " />
[1]
<state
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
representation="TXT
[0..1] "
mediaType="text/plain
[0..1] "
language="
cs
[0..1] "
partType="STA
[0..1] " />
[1]
<county
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
representation="TXT
[0..1] "
mediaType="text/plain
[0..1] "
language="
cs
[0..1] "
partType="CPA
[0..1] " />
[1]
<city
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
representation="TXT
[0..1] "
mediaType="text/plain
[0..1] "
language="
cs
[0..1] "
partType="CTY
[0..1] " />
[1]
<postalCode
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
representation="TXT
[0..1] "
mediaType="text/plain
[0..1] "
language="
cs
[0..1] "
partType="ZIP
[0..1] " />
[1]
<streetAddressLine
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
representation="TXT
[0..1] "
mediaType="text/plain
[0..1] "
language="
cs
[0..1] "
partType="SAL
[0..1] " />
[1]
<houseNumber
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
representation="TXT
[0..1] "
mediaType="text/plain
[0..1] "
language="
cs
[0..1] "
partType="BNR
[0..1] " />
[1]
<houseNumberNumeric
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
representation="TXT
[0..1] "
mediaType="text/plain
[0..1] "
language="
cs
[0..1] "
partType="BNN
[0..1] " />
[1]
<direction
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
representation="TXT
[0..1] "
mediaType="text/plain
[0..1] "
language="
cs
[0..1] "
partType="DIR
[0..1] " />
[1]
<streetName
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
representation="TXT
[0..1] "
mediaType="text/plain
[0..1] "
language="
cs
[0..1] "
partType="STR
[0..1] " />
[1]
<streetNameBase
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
representation="TXT
[0..1] "
mediaType="text/plain
[0..1] "
language="
cs
[0..1] "
partType="STB
[0..1] " />
[1]
<streetNameType
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
representation="TXT
[0..1] "
mediaType="text/plain
[0..1] "
language="
cs
[0..1] "
partType="STTYP
[0..1] " />
[1]
<additionalLocator
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
representation="TXT
[0..1] "
mediaType="text/plain
[0..1] "
language="
cs
[0..1] "
partType="ADL
[0..1] " />
[1]
<unitID
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
representation="TXT
[0..1] "
mediaType="text/plain
[0..1] "
language="
cs
[0..1] "
partType="UNID
[0..1] " />
[1]
<unitType
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
representation="TXT
[0..1] "
mediaType="text/plain
[0..1] "
language="
cs
[0..1] "
partType="UNIT
[0..1] " />
[1]
<carrier
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
representation="TXT
[0..1] "
mediaType="text/plain
[0..1] "
language="
cs
[0..1] "
partType="CAR
[0..1] " />
[1]
<censusTract
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
representation="TXT
[0..1] "
mediaType="text/plain
[0..1] "
language="
cs
[0..1] "
partType="CEN
[0..1] " />
[1]
End Choice
<useablePeriod>
SXCM_TS
</useablePeriod>
[0..*]
?
</...>
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
AD "
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:extension
base ="
ANY
">
<
xsd:sequence >
<
xsd:choice
minOccurs ="
0 "
maxOccurs ="
unbounded ">
<
xsd:element
name ="
delimiter ">
<
xsd:complexType
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
ADXP
">
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
</
xsd:element >
<
xsd:element
name ="
country ">
<
xsd:complexType
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
ADXP
">
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
</
xsd:element >
<
xsd:element
name ="
state ">
<
xsd:complexType
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
ADXP
">
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
</
xsd:element >
<
xsd:element
name ="
county ">
<
xsd:complexType
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
ADXP
">
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
</
xsd:element >
<
xsd:element
name ="
city ">
<
xsd:complexType
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
ADXP
">
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
</
xsd:element >
<
xsd:element
name ="
postalCode ">
<
xsd:complexType
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
ADXP
">
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
</
xsd:element >
<
xsd:element
name ="
streetAddressLine ">
<
xsd:complexType
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
ADXP
">
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
</
xsd:element >
<
xsd:element
name ="
houseNumber ">
<
xsd:complexType
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
ADXP
">
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
</
xsd:element >
<
xsd:element
name ="
houseNumberNumeric ">
<
xsd:complexType
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
ADXP
">
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
</
xsd:element >
<
xsd:element
name ="
direction ">
<
xsd:complexType
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
ADXP
">
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
</
xsd:element >
<
xsd:element
name ="
streetName ">
<
xsd:complexType
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
ADXP
">
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
</
xsd:element >
<
xsd:element
name ="
streetNameBase ">
<
xsd:complexType
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
ADXP
">
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
</
xsd:element >
<
xsd:element
name ="
streetNameType ">
<
xsd:complexType
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
ADXP
">
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
</
xsd:element >
<
xsd:element
name ="
additionalLocator ">
<
xsd:complexType
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
ADXP
">
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
</
xsd:element >
<
xsd:element
name ="
unitID ">
<
xsd:complexType
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
ADXP
">
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
</
xsd:element >
<
xsd:element
name ="
unitType ">
<
xsd:complexType
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
ADXP
">
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
</
xsd:element >
<
xsd:element
name ="
carrier ">
<
xsd:complexType
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
ADXP
">
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
</
xsd:element >
<
xsd:element
name ="
censusTract ">
<
xsd:complexType
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
ADXP
">
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
</
xsd:element >
</
xsd:choice >
<
xsd:element
name ="
useablePeriod "
type ="
SXCM_TS
"
minOccurs ="
0 "
maxOccurs ="
unbounded "></
xsd:element >
</
xsd:sequence >
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
isNotOrdered "
type ="
bl
"
use ="
optional "/>
</
xsd:extension >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
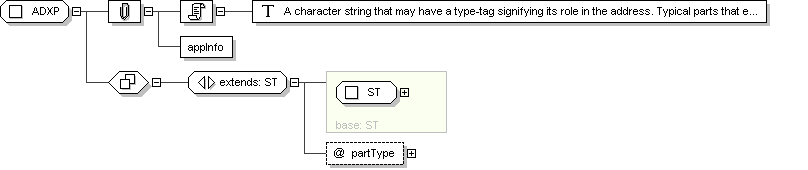
Complex Type: ADXP
Super-types:
ANY
<
BIN
(by extension) <
ED
(by extension) <
ST
(by restriction) < ADXP (by extension)
Sub-types:
None
Name
ADXP
Abstract
no
Documentation
A character string that may have a type-tag signifying its role in the
address. Typical parts that exist in about every address are street,
house number, or post box, postal code, city, country but other roles
may be defined regionally, nationally, or on an enterprise level
(e.g. in military addresses). Addresses are usually broken up into
lines, which are indicated by special line-breaking delimiter elements
(e.g., DEL).
Application Data
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
ADXP "
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:extension
base ="
ST
">
</
xsd:extension >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
Complex Type: ANY
Super-types:
None
Sub-types:
BL
(by extension)
BIN
(by extension)
CD
(by extension)
CE
(by restriction)
CV
(by restriction)
CS
(by restriction)
CO
(by extension)
PQR
(by extension)
CR
(by extension)
II
(by extension)
URL
(by extension)
AD
(by extension)
EN
(by extension)
PN
(by extension)
ON
(by restriction)
TN
(by restriction)
QTY
(by extension)
Name
ANY
Abstract
yes
Documentation
Defines the basic properties of every data value. This is an abstract
type, meaning that no value can be just a data value without belonging
to any concrete type. Every concrete type is a specialization of this
general abstract DataValue type.
Application Data
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
ANY "
abstract ="
true ">
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
nullFlavor "
type ="
cs_NullFlavor
"
use ="
optional "/>
</
xsd:complexType >
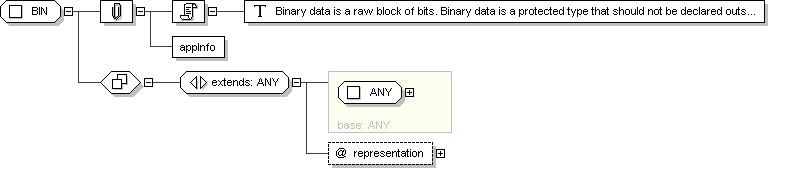
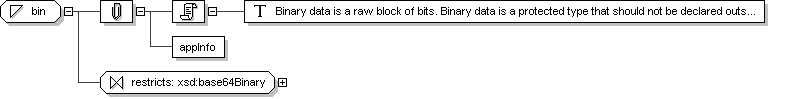
Complex Type: BIN
Super-types:
ANY
< BIN (by extension)
Sub-types:
Name
BIN
Abstract
yes
Documentation
Binary data is a raw block of bits. Binary data is a protected
type that should not be declared outside the data type specification.
Application Data
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
BIN "
abstract ="
true "
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:extension
base ="
ANY
">
</
xsd:extension >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
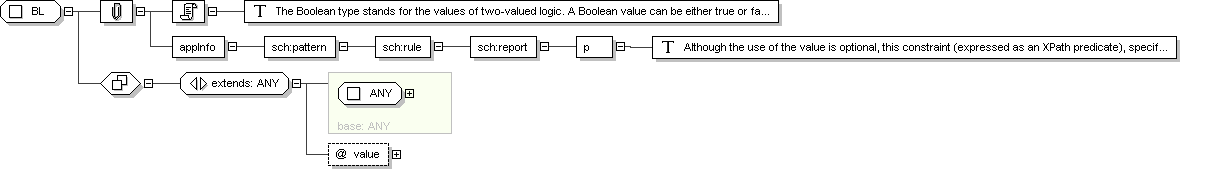
Complex Type: BL
Super-types:
ANY
< BL (by extension)
Sub-types:
None
Name
BL
Abstract
no
Documentation
The Boolean type stands for the values of two-valued logic. A
Boolean value can be either true or
false, or, as any other value may be NULL.
Application Data
<sch :pattern name="validate BL">
<sch :rule abstract="true" id="rule-BL">
<sch :report test="(@nullFlavor or @value) and not(@nullFlavor and @value)">
<p>
Although the use of the value is optional, this
constraint (expressed as an XPath predicate), specifies that there
must be either an value or the
attribute, but not both.
</p>
</sch :report>
</sch :rule>
</sch :pattern>
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
BL ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:extension
base ="
ANY
">
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
value "
type ="
bl
"
use ="
optional "/>
</
xsd:extension >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
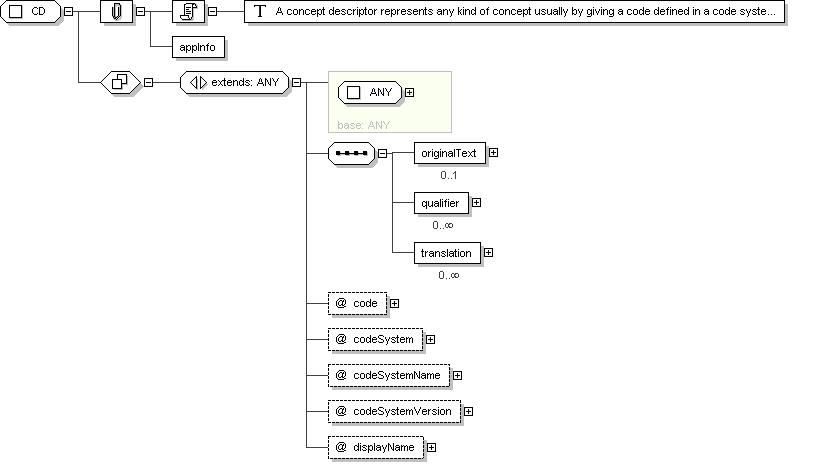
Complex Type: CD
Super-types:
ANY
< CD (by extension)
Sub-types:
CE
(by restriction)
CV
(by restriction)
CS
(by restriction)
CO
(by extension)
PQR
(by extension)
CR
(by extension)
Name
CD
Abstract
no
Documentation
A concept descriptor represents any kind of concept usually by
giving a code defined in a code system.
A concept descriptor can contain the original text or phrase that
served as the basis of the coding and one or more translations into
different coding systems.
A concept descriptor can also contain qualifiers to describe, e.g., the
concept of a "left foot" as a postcoordinated term built from the
primary code "FOOT" and the qualifier "LEFT".
In exceptional cases, the concept descriptor need not contain a code
but only the original text describing that concept.
Application Data
XML Instance Representation
<...
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
code="
cs
[0..1]
? "
codeSystem="
uid
[0..1]
? "
codeSystemName="
st
[0..1]
? "
codeSystemVersion="
st
[0..1]
? "
displayName="
st
[0..1]
? " >
<originalText>
ED
</originalText>
[0..1]
?
<qualifier>
CR
</qualifier>
[0..*]
?
<translation>
CD
</translation>
[0..*]
?
</...>
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
CD ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:extension
base ="
ANY
">
<
xsd:sequence >
<
xsd:element
name ="
originalText "
type ="
ED
"
minOccurs ="
0 "
maxOccurs ="
1 "/>
<
xsd:element
name ="
qualifier "
type ="
CR
"
minOccurs ="
0 "
maxOccurs ="
unbounded "/>
<
xsd:element
name ="
translation "
type ="
CD
"
minOccurs ="
0 "
maxOccurs ="
unbounded "/>
</
xsd:sequence >
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
code "
type ="
cs
"
use ="
optional "/>
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
codeSystem "
type ="
uid
"
use ="
optional "/>
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
codeSystemName "
type ="
st
"
use ="
optional "/>
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
codeSystemVersion "
type ="
st
"
use ="
optional "/>
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
displayName "
type ="
st
"
use ="
optional "/>
</
xsd:extension >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
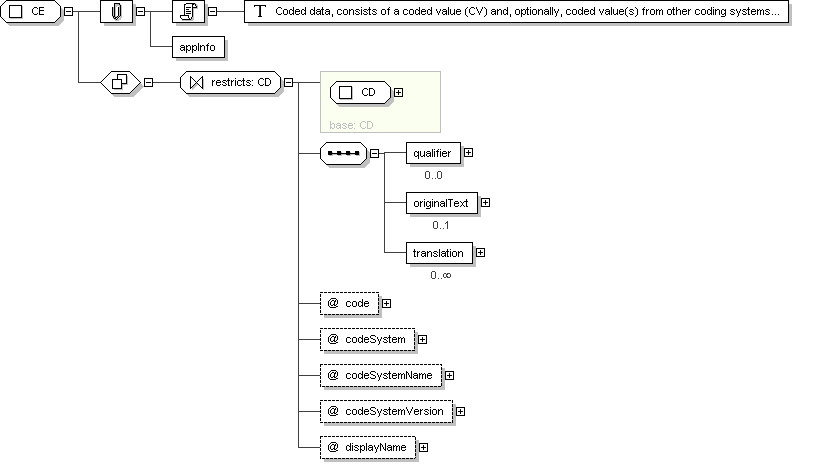
Complex Type: CE
Super-types:
ANY
<
CD
(by extension) < CE (by restriction)
Sub-types:
CV
(by restriction)
CS
(by restriction)
CO
(by extension)
PQR
(by extension)
Name
CE
Abstract
no
Documentation
Coded data, consists of a coded value (CV) and, optionally, coded
value(s) from other coding systems that identify the same
concept. Used when alternative codes may exist.
Application Data
XML Instance Representation
<...
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
code="
cs
[0..1]
? "
codeSystem="
uid
[0..1]
? "
codeSystemName="
st
[0..1]
? "
codeSystemVersion="
st
[0..1]
? "
displayName="
st
[0..1]
? " >
<originalText>
ED
</originalText>
[0..1]
?
<translation>
CD
</translation>
[0..*]
?
</...>
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
CE ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
CD
">
<
xsd:sequence >
<
xsd:element
name ="
qualifier "
type ="
CR
"
minOccurs ="
0 "
maxOccurs ="
0 "/>
<
xsd:element
name ="
originalText "
type ="
ED
"
minOccurs ="
0 "
maxOccurs ="
1 "/>
<
xsd:element
name ="
translation "
type ="
CD
"
minOccurs ="
0 "
maxOccurs ="
unbounded "/>
</
xsd:sequence >
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
code "
type ="
cs
"
use ="
optional "/>
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
codeSystem "
type ="
uid
"
use ="
optional "/>
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
codeSystemName "
type ="
st
"
use ="
optional "/>
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
codeSystemVersion "
type ="
st
"
use ="
optional "/>
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
displayName "
type ="
st
"
use ="
optional "/>
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
Complex Type: CO
Super-types:
ANY
<
CD
(by extension) <
CE
(by restriction) <
CV
(by restriction) < CO (by extension)
Sub-types:
None
Name
CO
Abstract
no
Documentation
Coded data, where the domain from which the codeset comes is ordered. The
Coded Ordinal data type adds semantics related to ordering so that models
that make use of such domains may introduce model elements that involve
statements about the order of the terms in a domain. The representation is
exactly the same as CV, but the type still needs to be defined.
Application Data
XML Instance Representation
<...
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
code="
cs
[0..1]
? "
codeSystem="
uid
[0..1]
? "
codeSystemName="
st
[0..1]
? "
codeSystemVersion="
st
[0..1]
? "
displayName="
st
[0..1]
? " >
<originalText>
ED
</originalText>
[0..1]
?
</...>
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
CO ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:extension
base ="
CV
"/>
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
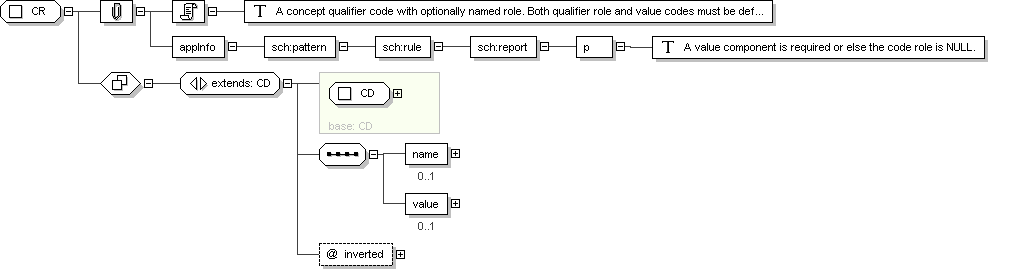
Complex Type: CR
Super-types:
ANY
<
CD
(by extension) < CR (by extension)
Sub-types:
None
Name
CR
Abstract
no
Documentation
A concept qualifier code with optionally named role. Both qualifier
role and value codes must be defined by the coding system. For
example, if SNOMED RT defines a concept "leg", a role relation
"has-laterality", and another concept "left", the concept role
relation allows to add the qualifier "has-laterality: left" to a
primary code "leg" to construct the meaning "left leg".
Application Data
<sch :pattern name="validate CR">
<sch :rule abstract="true" id="rule-CR">
<sch :report test="(value or @nullFlavor) and not(@nullFlavor and node())">
<p> A value component is required or else the code role is NULL.
</p>
</sch :report>
</sch :rule>
</sch :pattern>
XML Instance Representation
<...
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
code="
cs
[0..1]
? "
codeSystem="
uid
[0..1]
? "
codeSystemName="
st
[0..1]
? "
codeSystemVersion="
st
[0..1]
? "
displayName="
st
[0..1]
? "
inverted="
bl
[0..1]
? " >
<originalText>
ED
</originalText>
[0..1]
?
<qualifier>
CR
</qualifier>
[0..*]
?
<translation>
CD
</translation>
[0..*]
?
<name>
CV
</name>
[0..1]
?
<value>
CD
</value>
[0..1]
?
</...>
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
CR ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:extension
base ="
CD
">
<
xsd:sequence >
<
xsd:element
name ="
name "
type ="
CV
"
minOccurs ="
0 "
maxOccurs ="
1 "/>
<
xsd:element
name ="
value "
type ="
CD
"
minOccurs ="
0 "
maxOccurs ="
1 "/>
</
xsd:sequence >
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
inverted "
type ="
bl
"
use ="
optional "
default ="
false "/>
</
xsd:extension >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
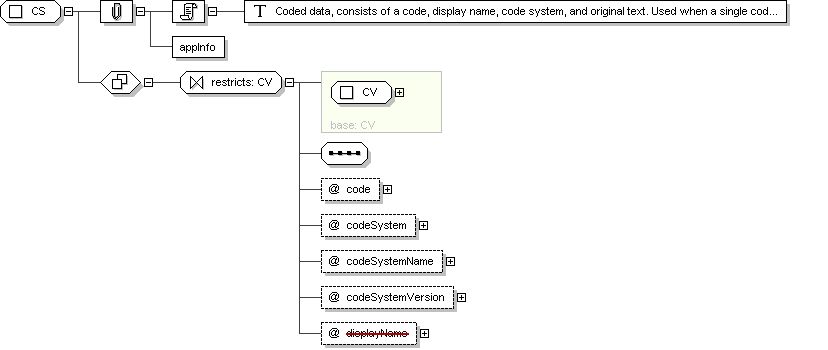
Complex Type: CS
Super-types:
ANY
<
CD
(by extension) <
CE
(by restriction) <
CV
(by restriction) < CS (by restriction)
Sub-types:
None
Name
CS
Abstract
no
Documentation
Coded data, consists of a code, display name, code system, and
original text. Used when a single code value must be sent.
Application Data
XML Instance Representation
<...
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
code="
cs
[0..1]
? "
codeSystem="
uid
[0..1] "
codeSystemName="
st
[0..1] "
codeSystemVersion="
st
[0..1] " />
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
CS ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
CV
">
<xsd:sequence />
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
code "
type ="
cs
"
use ="
optional "/>
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
codeSystem "
type ="
uid
"/>
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
codeSystemName "
type ="
st
"/>
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
codeSystemVersion "
type ="
st
"/>
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
displayName "
type ="
st
"
use ="
prohibited "/>
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
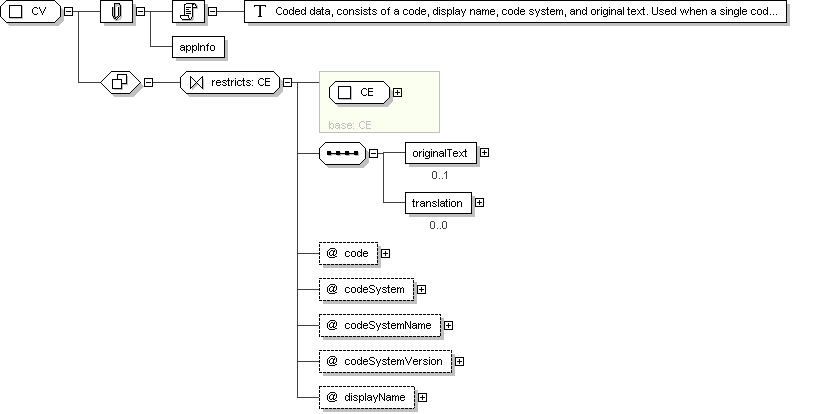
Complex Type: CV
Super-types:
ANY
<
CD
(by extension) <
CE
(by restriction) < CV (by restriction)
Sub-types:
CS
(by restriction)
CO
(by extension)
PQR
(by extension)
Name
CV
Abstract
no
Documentation
Coded data, consists of a code, display name, code system, and
original text. Used when a single code value must be sent.
Application Data
XML Instance Representation
<...
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
code="
cs
[0..1]
? "
codeSystem="
uid
[0..1]
? "
codeSystemName="
st
[0..1]
? "
codeSystemVersion="
st
[0..1]
? "
displayName="
st
[0..1]
? " >
<originalText>
ED
</originalText>
[0..1]
?
</...>
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
CV ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
CE
">
<
xsd:sequence >
<
xsd:element
name ="
originalText "
type ="
ED
"
minOccurs ="
0 "
maxOccurs ="
1 "/>
<
xsd:element
name ="
translation "
type ="
CD
"
minOccurs ="
0 "
maxOccurs ="
0 "/>
</
xsd:sequence >
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
code "
type ="
cs
"
use ="
optional "/>
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
codeSystem "
type ="
uid
"
use ="
optional "/>
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
codeSystemName "
type ="
st
"
use ="
optional "/>
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
codeSystemVersion "
type ="
st
"
use ="
optional "/>
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
displayName "
type ="
st
"
use ="
optional "/>
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
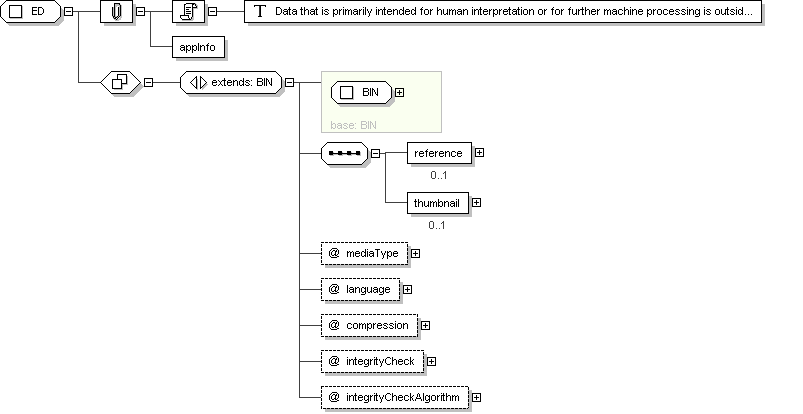
Complex Type: ED
Super-types:
ANY
<
BIN
(by extension) < ED (by extension)
Sub-types:
Name
ED
Abstract
no
Documentation
Data that is primarily intended for human interpretation or for
further machine processing is outside the scope of HL7. This includes
unformatted or formatted written language, multimedia data, or
structured information as defined by a different standard (e.g.,
XML-signatures.) Instead of the data itself, an ED
may contain only a reference (see TEL.) Note that
the ST data type is a specialization of the
ED data type when the ED
media type is text/plain.
Application Data
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
ED "
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:extension
base ="
BIN
">
<
xsd:sequence >
<
xsd:element
name ="
reference "
type ="
TEL
"
minOccurs ="
0 "
maxOccurs ="
1 "/>
<
xsd:element
name ="
thumbnail "
type ="
thumbnail
"
minOccurs ="
0 "
maxOccurs ="
1 "/>
</
xsd:sequence >
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
mediaType "
type ="
cs
"
use ="
optional "
default ="
text/plain "/>
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
language "
type ="
cs
"
use ="
optional "/>
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
integrityCheck "
type ="
bin
"
use ="
optional "/>
</
xsd:extension >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
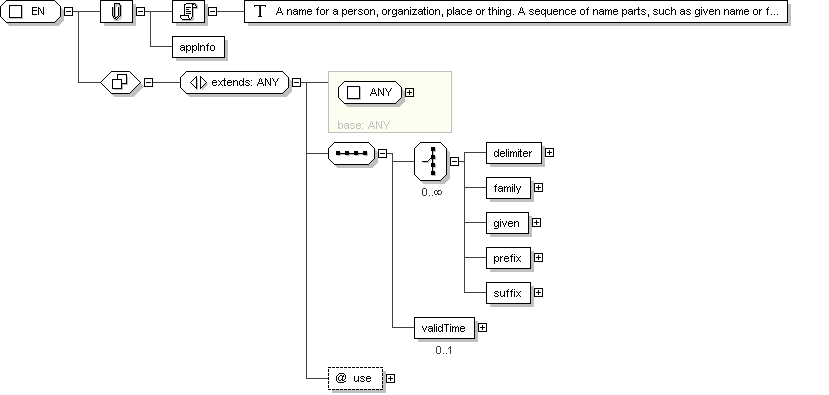
Complex Type: EN
Super-types:
ANY
< EN (by extension)
Sub-types:
PN
(by extension)
ON
(by restriction)
TN
(by restriction)
Name
EN
Abstract
no
Documentation
A name for a person, organization, place or thing. A sequence of name
parts, such as given name or family name, prefix, suffix, etc.
Examples for entity name values are "Jim Bob Walton, Jr.", "Health
Level Seven, Inc.", "Lake Tahoe", etc. An entity name may be as simple
as a character string or may consist of several entity name parts,
such as, "Jim", "Bob", "Walton", and "Jr.", "Health Level Seven" and
"Inc.", "Lake" and "Tahoe".
Application Data
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
EN "
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:extension
base ="
ANY
">
<
xsd:sequence >
<
xsd:choice
minOccurs ="
0 "
maxOccurs ="
unbounded ">
<
xsd:element
name ="
family "
type ="
en.family
"/>
<
xsd:element
name ="
given "
type ="
en.given
"/>
<
xsd:element
name ="
prefix "
type ="
en.prefix
"/>
<
xsd:element
name ="
suffix "
type ="
en.suffix
"/>
</
xsd:choice >
<
xsd:element
name ="
validTime "
type ="
IVL_TS
"
minOccurs ="
0 "
maxOccurs ="
1 "/>
</
xsd:sequence >
</
xsd:extension >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
Super-types:
ANY
<
BIN
(by extension) <
ED
(by extension) <
ST
(by restriction) <
ENXP
(by extension) < en.delimiter (by restriction)
Sub-types:
None
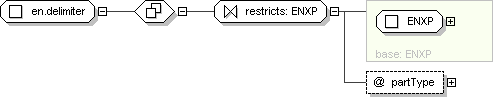
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
en.delimiter "
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
ENXP
">
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
Super-types:
ANY
<
BIN
(by extension) <
ED
(by extension) <
ST
(by restriction) <
ENXP
(by extension) < en.family (by restriction)
Sub-types:
None
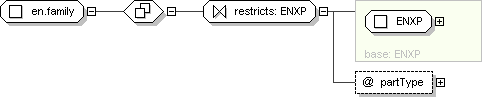
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
en.family "
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
ENXP
">
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
Super-types:
ANY
<
BIN
(by extension) <
ED
(by extension) <
ST
(by restriction) <
ENXP
(by extension) < en.given (by restriction)
Sub-types:
None
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
en.given "
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
ENXP
">
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
Super-types:
ANY
<
BIN
(by extension) <
ED
(by extension) <
ST
(by restriction) <
ENXP
(by extension) < en.prefix (by restriction)
Sub-types:
None
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
en.prefix "
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
ENXP
">
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
Super-types:
ANY
<
BIN
(by extension) <
ED
(by extension) <
ST
(by restriction) <
ENXP
(by extension) < en.suffix (by restriction)
Sub-types:
None
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
en.suffix "
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
ENXP
">
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
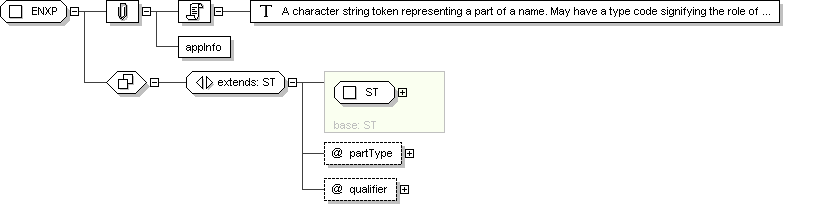
Complex Type: ENXP
Super-types:
ANY
<
BIN
(by extension) <
ED
(by extension) <
ST
(by restriction) < ENXP (by extension)
Sub-types:
Name
ENXP
Abstract
no
Documentation
A character string token representing a part of a name. May have a
type code signifying the role of the part in the whole entity name,
and a qualifier code for more detail about the name part type.
Typical name parts for person names are given names, and family names,
titles, etc.
Application Data
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
ENXP "
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:extension
base ="
ST
">
</
xsd:extension >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
Complex Type: II
Super-types:
ANY
< II (by extension)
Sub-types:
None
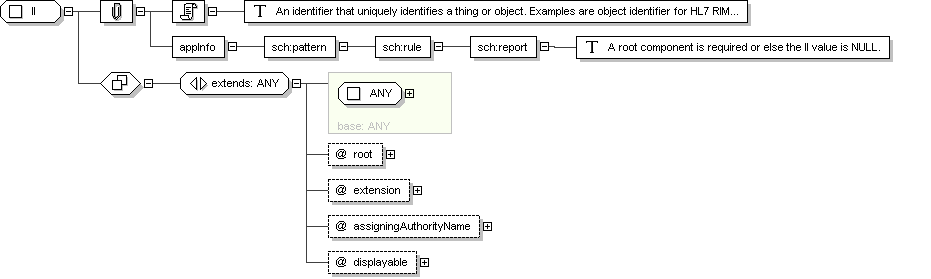
Name
II
Abstract
no
Documentation
An identifier that uniquely identifies a thing or object. Examples
are object identifier for HL7 RIM objects, medical record number,
order id, service catalog item id, Vehicle Identification Number
(VIN), etc. Instance identifiers are defined based on ISO object
identifiers.
Application Data
<sch :pattern name="validate II">
<sch :rule abstract="true" id="rule-II">
<sch :report test="(@root or @nullFlavor) and not(@root and @nullFlavor)">
A root component is required or else the II value is NULL.
</sch :report>
</sch :rule>
</sch :pattern>
XML Instance Representation
<...
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
root="
uid
[0..1]
? "
extension="
st
[0..1]
? "
assigningAuthorityName="
st
[0..1]
? "
displayable="
bl
[0..1]
? " />
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
II ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:extension
base ="
ANY
">
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
root "
type ="
uid
"
use ="
optional "/>
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
extension "
type ="
st
"
use ="
optional "/>
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
assigningAuthorityName "
type ="
st
"
use ="
optional "/>
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
displayable "
type ="
bl
"
use ="
optional "/>
</
xsd:extension >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
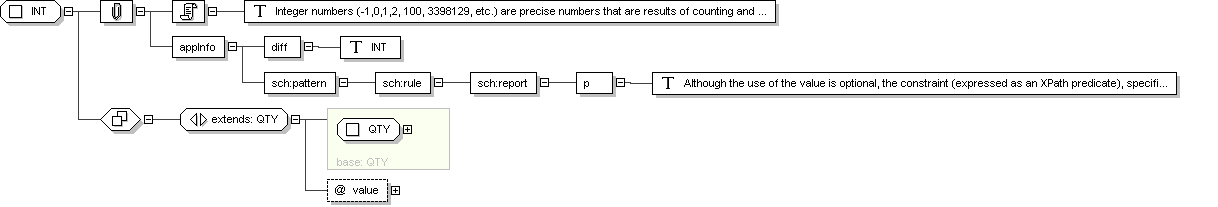
Complex Type: INT
Super-types:
ANY
<
QTY
(by extension) < INT (by extension)
Sub-types:
None
Name
INT
Abstract
no
Documentation
Integer numbers (-1,0,1,2, 100, 3398129, etc.) are precise numbers
that are results of counting and enumerating. Integer numbers are
discrete, the set of integers is infinite but countable. No arbitrary
limit is imposed on the range of integer numbers. Two NULL flavors are
defined for the positive and negative infinity.
Application Data
<diff> INT
</diff>
<sch :pattern name="validate INT">
<sch :rule abstract="true" id="rule-INT">
<sch :report test="(@value or @nullFlavor) and not(@value and @nullFlavor)">
<p>
Although the use of the value is optional, the constraint
(expressed as an XPath predicate), specifies that there must be either
an value or the , but
not both.
</p>
</sch :report>
</sch :rule>
</sch :pattern>
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
INT ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:extension
base ="
QTY
">
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
value "
type ="
int
"
use ="
optional "/>
</
xsd:extension >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
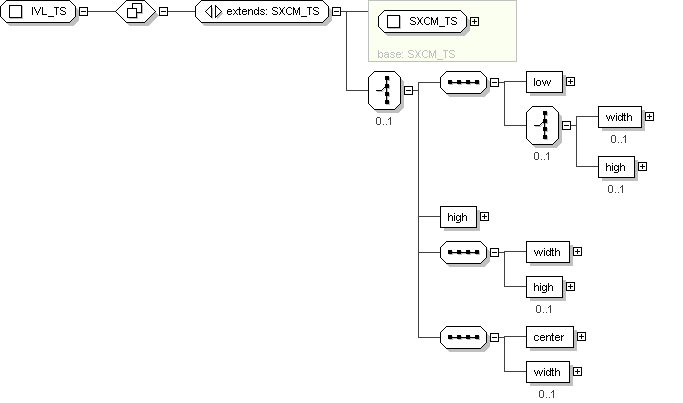
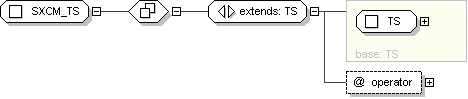
Complex Type: IVL_TS
Super-types:
ANY
<
QTY
(by extension) <
TS
(by extension) <
SXCM_TS
(by extension) < IVL_TS (by extension)
Sub-types:
None
XML Instance Representation
<...
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
value="
ts
[0..1] "
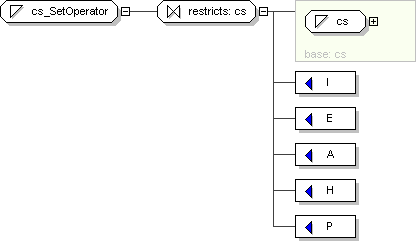
operator="
cs_SetOperator
[0..1]
? " >
Start Choice
[0..1]
Start Choice
[0..1]
<width>
PQ
</width>
[0..1]
?
End Choice
<width>
PQ
</width>
[1]
?
<center>
TS
</center>
[1]
?
<width>
PQ
</width>
[0..1]
?
End Choice
</...>
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
IVL_TS ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:extension
base ="
SXCM_TS
">
<
xsd:choice
minOccurs ="
0 ">
<
xsd:sequence >
<
xsd:element
name ="
low "
type ="
IVXB_TS
"
minOccurs ="
1 "
maxOccurs ="
1 "/>
<
xsd:choice
minOccurs ="
0 ">
<
xsd:element
name ="
width "
type ="
PQ
"
minOccurs ="
0 "
maxOccurs ="
1 "/>
<
xsd:element
name ="
high "
type ="
IVXB_TS
"
minOccurs ="
0 "
maxOccurs ="
1 "/>
</
xsd:choice >
</
xsd:sequence >
<
xsd:element
name ="
high "
type ="
IVXB_TS
"
minOccurs ="
1 "
maxOccurs ="
1 "/>
<
xsd:sequence >
<
xsd:element
name ="
width "
type ="
PQ
"
minOccurs ="
1 "
maxOccurs ="
1 "/>
<
xsd:element
name ="
high "
type ="
IVXB_TS
"
minOccurs ="
0 "
maxOccurs ="
1 "/>
</
xsd:sequence >
<
xsd:sequence >
<
xsd:element
name ="
center "
type ="
TS
"
minOccurs ="
1 "
maxOccurs ="
1 "/>
<
xsd:element
name ="
width "
type ="
PQ
"
minOccurs ="
0 "
maxOccurs ="
1 "/>
</
xsd:sequence >
</
xsd:choice >
</
xsd:extension >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
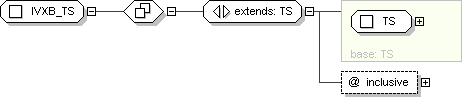
Super-types:
ANY
<
QTY
(by extension) <
TS
(by extension) < IVXB_TS (by extension)
Sub-types:
None
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
IVXB_TS ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:extension
base ="
TS
">
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
inclusive "
type ="
bl
"
use ="
optional "
default ="
true "/>
</
xsd:extension >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
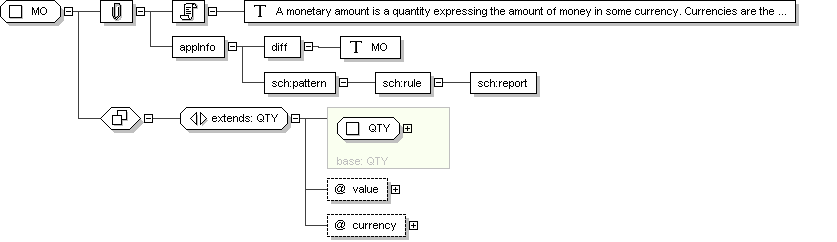
Complex Type: MO
Super-types:
ANY
<
QTY
(by extension) < MO (by extension)
Sub-types:
None
Name
MO
Abstract
no
Documentation
A monetary amount is a quantity expressing the amount of money in some
currency. Currencies are the units in which monetary amounts are
denominated in different economic regions. While the monetary amount
is a single kind of quantity (money) the exchange rates between the
different units are variable. This is the principle difference
between physical quantity and monetary amounts, and the reason why
currency units are not physical units.
Application Data
<diff> MO
</diff>
<sch :pattern name="validate MO">
<sch :rule abstract="true" id="rule-MO">
<sch :report test="not(@nullFlavor and (@value or @currency))"/>
</sch :rule>
</sch :pattern>
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
MO ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:extension
base ="
QTY
">
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
value "
type ="
real
"
use ="
optional "/>
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
currency "
type ="
cs
"
use ="
optional "/>
</
xsd:extension >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
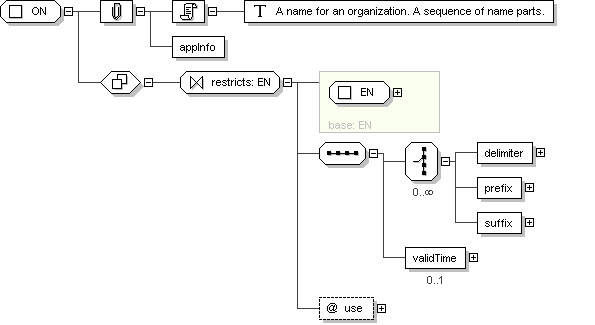
Complex Type: ON
Super-types:
ANY
<
EN
(by extension) < ON (by restriction)
Sub-types:
None
Name
ON
Abstract
no
Documentation
A name for an organization. A sequence of name parts.
Application Data
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
ON "
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
EN
">
<
xsd:sequence >
<
xsd:choice
minOccurs ="
0 "
maxOccurs ="
unbounded ">
<
xsd:element
name ="
prefix "
type ="
en.prefix
"/>
<
xsd:element
name ="
suffix "
type ="
en.suffix
"/>
</
xsd:choice >
<
xsd:element
name ="
validTime "
type ="
IVL_TS
"
minOccurs ="
0 "
maxOccurs ="
1 "/>
</
xsd:sequence >
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
Complex Type: PN
Super-types:
ANY
<
EN
(by extension) < PN (by extension)
Sub-types:
None
Name
PN
Abstract
no
Documentation
A name for a person. A sequence of name parts, such as given name or family name, prefix, suffix, etc. PN differs from
EN because the qualifier type cannot include LS (Legal Status).
Application Data
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
PN "
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:extension
base ="
EN
"/>
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
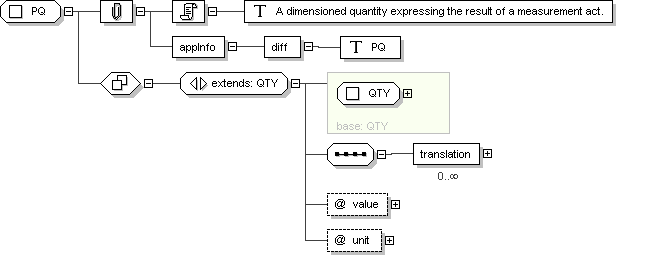
Complex Type: PQ
Super-types:
ANY
<
QTY
(by extension) < PQ (by extension)
Sub-types:
None
Name
PQ
Abstract
no
Documentation
A dimensioned quantity expressing the result of a measurement act.
Application Data
<diff> PQ
</diff>
XML Instance Representation
<...
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
value="
real
[0..1]
? "
unit="
cs
[0..1]
? " >
<translation>
PQR
</translation>
[0..*]
?
</...>
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
PQ ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:extension
base ="
QTY
">
<
xsd:sequence >
<
xsd:element
name ="
translation "
type ="
PQR
"
minOccurs ="
0 "
maxOccurs ="
unbounded "/>
</
xsd:sequence >
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
value "
type ="
real
"
use ="
optional "/>
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
unit "
type ="
cs
"
use ="
optional "
default ="
1 "/>
</
xsd:extension >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
Complex Type: PQR
Super-types:
ANY
<
CD
(by extension) <
CE
(by restriction) <
CV
(by restriction) < PQR (by extension)
Sub-types:
None
Name
PQR
Abstract
no
Documentation
A representation of a physical quantity in a unit from any code
system. Used to show alternative representation for a physical
quantity.
Application Data
XML Instance Representation
<...
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
code="
cs
[0..1]
? "
codeSystem="
uid
[0..1]
? "
codeSystemName="
st
[0..1]
? "
codeSystemVersion="
st
[0..1]
? "
displayName="
st
[0..1]
? "
value="
real
[0..1]
? " >
<originalText>
ED
</originalText>
[0..1]
?
</...>
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
PQR ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:extension
base ="
CV
">
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
value "
type ="
real
"
use ="
optional "/>
</
xsd:extension >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
Complex Type: QTY
Super-types:
ANY
< QTY (by extension)
Sub-types:
Name
QTY
Abstract
yes
Documentation
The quantity data type is an abstract generalization for all data
types (1) whose value set has an order relation (less-or-equal) and
(2) where difference is defined in all of the data type's totally
ordered value subsets. The quantity type abstraction is needed in
defining certain other types, such as the interval and the probability
distribution.
Application Data
<diff> QTY
</diff>
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
QTY "
abstract ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:extension
base ="
ANY
"/>
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
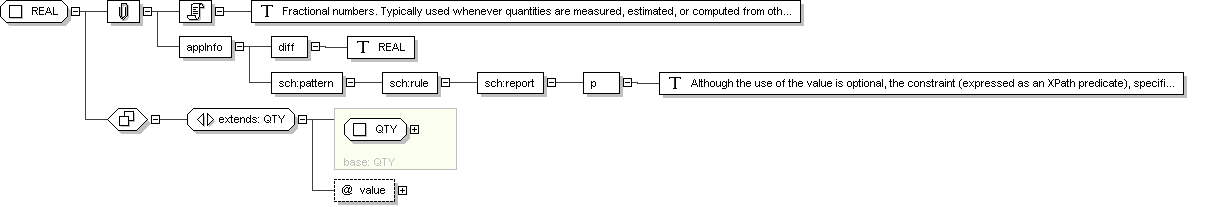
Complex Type: REAL
Super-types:
ANY
<
QTY
(by extension) < REAL (by extension)
Sub-types:
None
Name
REAL
Abstract
no
Documentation
Fractional numbers. Typically used whenever quantities are measured,
estimated, or computed from other real numbers. The typical
representation is decimal, where the number of significant decimal
digits is known as the precision.
Real numbers are needed beyond integers whenever quantities of the
real world are measured, estimated, or computed from other real
numbers. The term "Real number" in this specification is used to mean
that fractional values are covered without necessarily implying the
full set of the mathematical real numbers.
Application Data
<diff> REAL
</diff>
<sch :pattern name="validate REAL">
<sch :rule abstract="true" id="rule-REAL">
<sch :report test="(@nullFlavor or @value) and not(@nullFlavor and @value)">
<p>
Although the use of the value is optional, the
constraint (expressed as an XPath predicate), specifies that there
must be either a value or the
, but not both.
</p>
</sch :report>
</sch :rule>
</sch :pattern>
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
REAL ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:extension
base ="
QTY
">
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
value "
type ="
real
"
use ="
optional "/>
</
xsd:extension >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
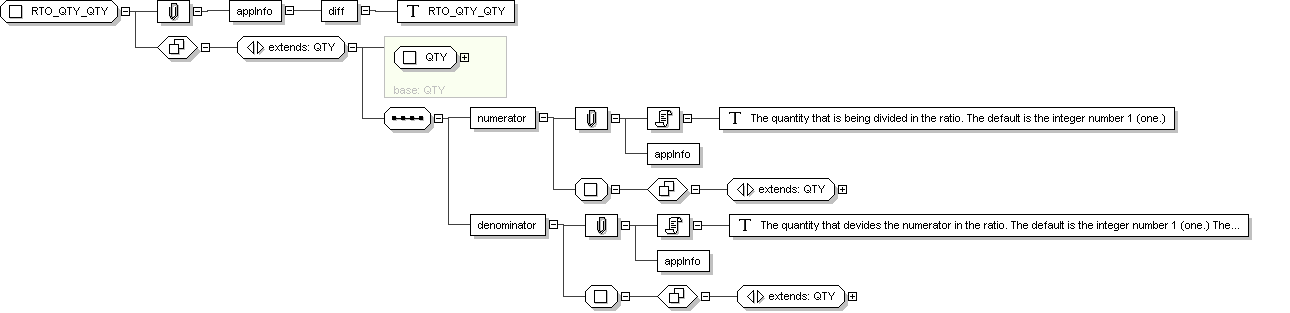
Complex Type: RTO
Super-types:
ANY
<
QTY
(by extension) <
RTO_QTY_QTY
(by extension) < RTO (by extension)
Sub-types:
None
Name
RTO
Abstract
no
Documentation
A quantity constructed as the quotient of a numerator quantity divided
by a denominator quantity. Common factors in the numerator and
denominator are not automatically cancelled out. The data
type supports titers (e.g., "1:128") and other quantities produced by
laboratories that truly represent ratios. Ratios are not simply
"structured numerics", particularly blood pressure measurements
(e.g. "120/60") are not ratios. In many cases the
REAL should be used instead of the
.
Application Data
XML Instance Representation
<...
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? " >
<numerator
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
value="anySimpleType
[0..1] " />
[1]
?
<denominator
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
value="anySimpleType
[0..1] " />
[1]
?
</...>
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
RTO ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
Super-types:
ANY
<
QTY
(by extension) < RTO_QTY_QTY (by extension)
Sub-types:
Name
RTO_QTY_QTY
Abstract
no
Application Data
<diff> RTO_QTY_QTY
</diff>
XML Instance Representation
<...
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? " >
<numerator
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
value="anySimpleType
[0..1] " />
[1]
?
<denominator
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
value="anySimpleType
[0..1] " />
[1]
?
</...>
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
RTO_QTY_QTY ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:extension
base ="
QTY
">
<
xsd:sequence >
<
xsd:element
name ="
numerator ">
<
xsd:complexType >
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:extension
base ="
QTY
">
<xsd:attribute
name ="value " default ="1 "/>
</
xsd:extension >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
</
xsd:element >
<
xsd:element
name ="
denominator ">
<
xsd:complexType >
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:extension
base ="
QTY
">
<xsd:attribute
name ="value " default ="1 "/>
</
xsd:extension >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
</
xsd:element >
</
xsd:sequence >
</
xsd:extension >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
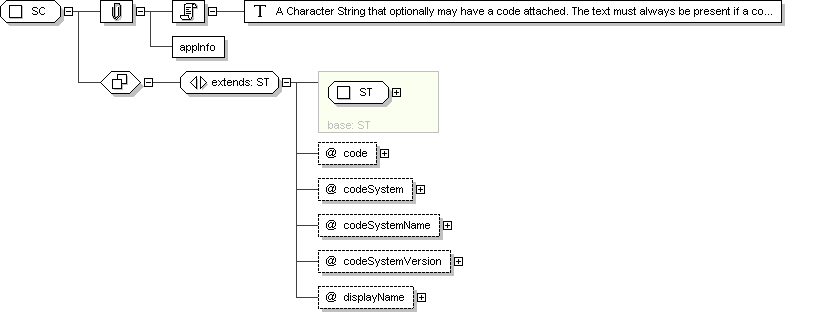
Complex Type: SC
Super-types:
ANY
<
BIN
(by extension) <
ED
(by extension) <
ST
(by restriction) < SC (by extension)
Sub-types:
None
Name
SC
Abstract
no
Documentation
A Character String that optionally
may have a code attached. The text must always be present if a code is
present. The code is often a local code.
Application Data
XML Instance Representation
<...
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
representation="TXT
[0..1] "
mediaType="text/plain
[0..1] "
language="
cs
[0..1] "
code="
cs
[0..1]
? "
codeSystem="
uid
[0..1]
? "
codeSystemName="
st
[0..1]
? "
codeSystemVersion="
st
[0..1]
? "
displayName="
st
[0..1]
? " />
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
SC "
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:extension
base ="
ST
">
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
code "
type ="
cs
"
use ="
optional "/>
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
codeSystem "
type ="
uid
"
use ="
optional "/>
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
codeSystemName "
type ="
st
"
use ="
optional "/>
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
codeSystemVersion "
type ="
st
"
use ="
optional "/>
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
displayName "
type ="
st
"
use ="
optional "/>
</
xsd:extension >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
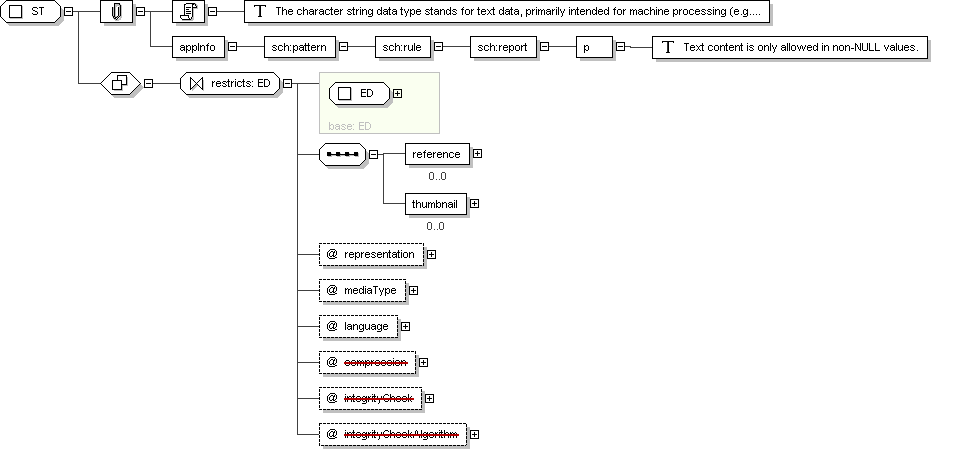
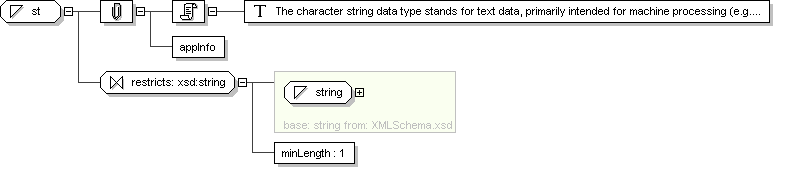
Complex Type: ST
Super-types:
ANY
<
BIN
(by extension) <
ED
(by extension) < ST (by restriction)
Sub-types:
SC
(by extension)
ADXP
(by extension)
ENXP
(by extension)
Name
ST
Abstract
no
Documentation
The character string data type stands for text data, primarily
intended for machine processing (e.g., sorting, querying, indexing,
etc.) Used for names, symbols, and formal expressions.
Application Data
<sch :pattern name="validate ST">
<sch :rule abstract="true" id="rule-ST">
<sch :report test="(@nullFlavor or text()) and not(@nullFlavor and text())">
<p> Text content is only allowed in non-NULL values.
</p>
</sch :report>
</sch :rule>
</sch :pattern>
XML Instance Representation
<...
nullFlavor="
cs_NullFlavor
[0..1]
? "
representation="TXT
[0..1] "
mediaType="text/plain
[0..1] "
language="
cs
[0..1] " />
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
ST "
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
ED
">
<
xsd:sequence >
<
xsd:element
name ="
reference "
type ="
TEL
"
minOccurs ="
0 "
maxOccurs ="
0 "/>
<
xsd:element
name ="
thumbnail "
type ="
ED
"
minOccurs ="
0 "
maxOccurs ="
0 "/>
</
xsd:sequence >
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
mediaType "
type ="
cs
"
fixed ="
text/plain "/>
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
language "
type ="
cs
"
use ="
optional "/>
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
integrityCheck "
type ="
bin
"
use ="
prohibited "/>
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
Super-types:
ANY
<
QTY
(by extension) <
TS
(by extension) < SXCM_TS (by extension)
Sub-types:
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
SXCM_TS ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:extension
base ="
TS
">
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
operator "
type ="
cs_SetOperator
"
use ="
optional "
default ="
I "/>
</
xsd:extension >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
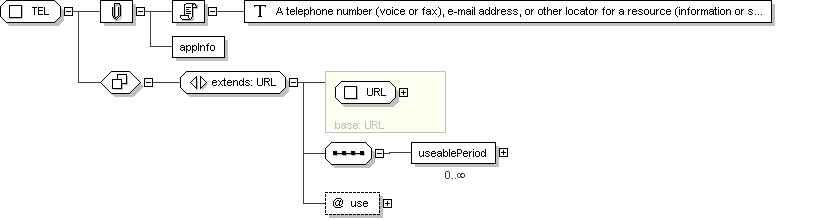
Complex Type: TEL
Super-types:
ANY
<
URL
(by extension) < TEL (by extension)
Sub-types:
None
Name
TEL
Abstract
no
Documentation
A telephone number (voice or fax), e-mail address, or other locator
for a resource (information or service) mediated by telecommunication
equipment. The address is specified as a Universal Resource Locator
(URL) qualified by time specification and use codes that help in
deciding which address to use for a given time and purpose.
Application Data
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
TEL ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:extension
base ="
URL
">
<
xsd:sequence >
<
xsd:element
name ="
useablePeriod "
type ="
SXCM_TS
"
minOccurs ="
0 "
maxOccurs ="
unbounded "></
xsd:element >
</
xsd:sequence >
</
xsd:extension >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
Super-types:
ANY
<
BIN
(by extension) <
ED
(by extension) < thumbnail (by restriction)
Sub-types:
None
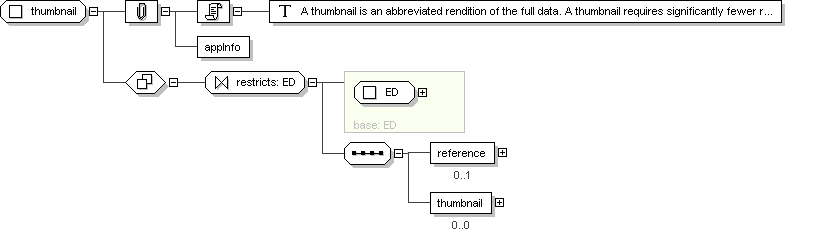
Name
thumbnail
Abstract
no
Documentation
A thumbnail is an abbreviated rendition of the full data. A thumbnail
requires significantly fewer resources than the full data, while still
maintaining some distinctive similarity with the full data. A
thumbnail is typically used with by-reference encapsulated data. It
allows a user to select data more efficiently before actually
downloading through the reference.
Application Data
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
thumbnail ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
ED
">
<
xsd:sequence >
<
xsd:element
name ="
reference "
type ="
TEL
"
minOccurs ="
0 "
maxOccurs ="
1 "/>
<
xsd:element
name ="
thumbnail "
type ="
thumbnail
"
minOccurs ="
0 "
maxOccurs ="
0 "/>
</
xsd:sequence >
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
Complex Type: TN
Super-types:
ANY
<
EN
(by extension) < TN (by restriction)
Sub-types:
None
Name
TN
Abstract
no
Documentation
A restriction of entity name that is effectively a simple string used
for a simple name for things and places.
Application Data
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
TN "
mixed ="
true ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
EN
">
<xsd:sequence ></xsd:sequence >
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
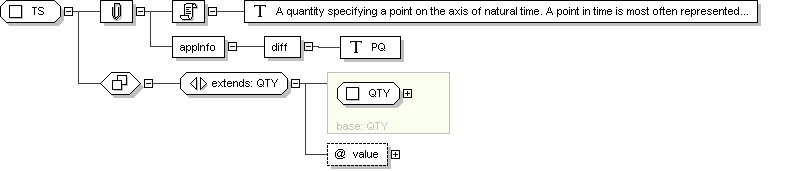
Complex Type: TS
Super-types:
ANY
<
QTY
(by extension) < TS (by extension)
Sub-types:
Name
TS
Abstract
no
Documentation
A quantity specifying a point on the axis of natural time. A point
in time is most often represented as a calendar expression.
Application Data
<diff> PQ
</diff>
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
TS ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:extension
base ="
QTY
">
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
value "
type ="
ts
"
use ="
optional "/>
</
xsd:extension >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
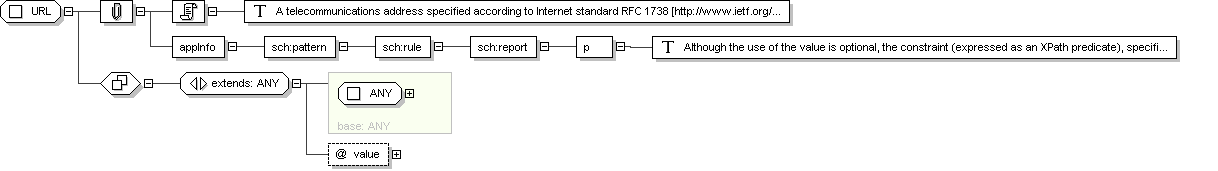
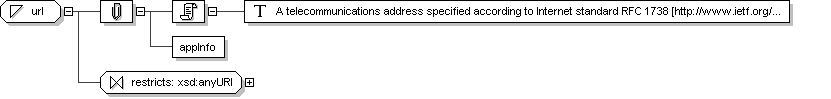
Complex Type: URL
Super-types:
ANY
< URL (by extension)
Sub-types:
Name
URL
Abstract
no
Documentation
A telecommunications address specified according to Internet standard
RFC 1738 [http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc1738.txt]. The
URL specifies the protocol and the contact point defined by that
protocol for the resource. Notable uses of the telecommunication
address data type are for telephone and telefax numbers, e-mail
addresses, Hypertext references, FTP references, etc.
Application Data
<sch :pattern name="validate URL">
<sch :rule abstract="true" id="rule-URL">
<sch :report test="(@nullFlavor or @value) and not(@nullFlavor and @value)">
<p>
Although the use of the value is optional, the
constraint (expressed as an XPath predicate), specifies that there
must be either an value or the
attribute, but not both.
</p>
</sch :report>
</sch :rule>
</sch :pattern>
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:complexType
name ="
URL ">
<
xsd:complexContent >
<
xsd:extension
base ="
ANY
">
<
xsd:attribute
name ="
value "
type ="
url
"
use ="
optional "/>
</
xsd:extension >
</
xsd:complexContent >
</
xsd:complexType >
Simple Type: bin
Super-types:
xsd :base64Binary < bin (by restriction)
Sub-types:
None
Name
bin
Content
Base XSD Type: base64Binary
Documentation
Binary data is a raw block of bits. Binary data is a protected
type that should not be declared outside the data type specification.
Application Data
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:simpleType
name ="
bin ">
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
xsd :base64Binary
"/>
</
xsd:simpleType >
Simple Type: bl
Super-types:
xsd :boolean < bl (by restriction)
Sub-types:
Name
bl
Content
Documentation
The Boolean type stands for the values of two-valued logic. A
Boolean value can be either true or
false, or, as any other value may be NULL.
Application Data
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:simpleType
name ="
bl ">
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
xsd :boolean
">
<xsd:pattern
value ="true|false "/>
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:simpleType >
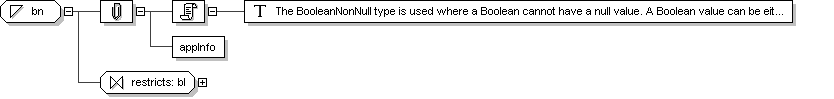
Simple Type: bn
Super-types:
xsd :boolean <
bl
(by restriction) < bn (by restriction)
Sub-types:
None
Name
bn
Content
Documentation
The BooleanNonNull type is used where a Boolean cannot have a null value. A
Boolean value can be either true or
false.
Application Data
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:simpleType
name ="
bn ">
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
bl
"/>
</
xsd:simpleType >
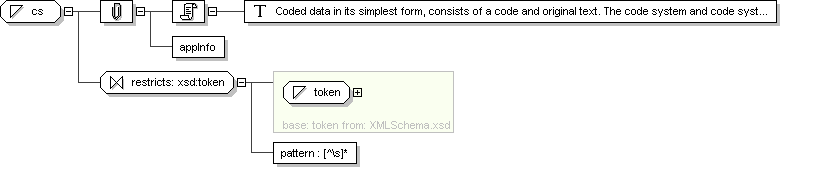
Simple Type: cs
Super-types:
xsd :token < cs (by restriction)
Sub-types:
Name
cs
Content
Documentation
Coded data in its simplest form, consists of a code and original text.
The code system and code system version is fixed by the context in
which the CS value occurs. CS is used for coded attributes that have a
single HL7-defined value set.
Application Data
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:simpleType
name ="
cs ">
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
xsd :token
">
<xsd:pattern
value ="[^\s]* "/>
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:simpleType >
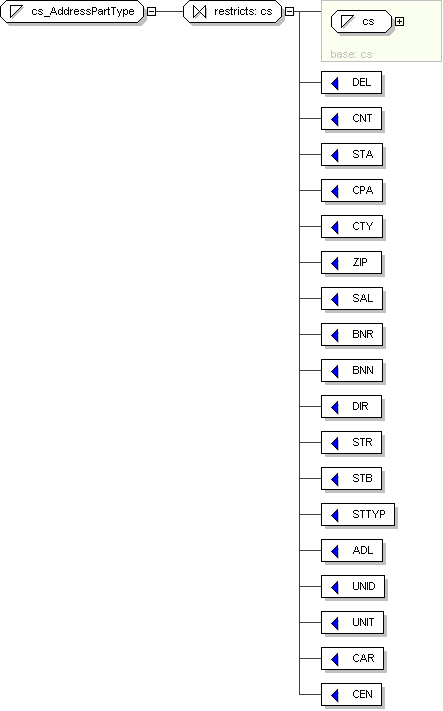
Super-types:
xsd :token <
cs
(by restriction) < cs_AddressPartType (by restriction)
Sub-types:
None
Name
cs_AddressPartType
Content
value comes from list: {'DEL'|'CNT'|'STA'|'CPA'|'CTY'|'ZIP'|'SAL'|'BNR'|'BNN'|'DIR'|'STR'|'STB'|'STTYP'|'ADL'|'UNID'|'UNIT'|'CAR'|'CEN'}
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:simpleType
name ="
cs_AddressPartType ">
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
cs
">
<xsd:enumeration
value ="DEL "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="CNT "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="STA "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="CPA "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="CTY "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="ZIP "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="SAL "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="BNR "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="BNN "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="DIR "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="STR "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="STB "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="STTYP "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="ADL "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="UNID "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="UNIT "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="CAR "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="CEN "/>
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:simpleType >
Super-types:
xsd :NMTOKEN < cs_BinaryDataEncoding (by restriction)
Sub-types:
None
Name
cs_BinaryDataEncoding
Content
value comes from list: {'B64'|'TXT'}
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:simpleType
name ="
cs_BinaryDataEncoding ">
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
xsd :NMTOKEN
">
<xsd:enumeration
value ="B64 "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="TXT "/>
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:simpleType >
Super-types:
xsd :token <
cs
(by restriction) < cs_CalendarCycle (by restriction)
Sub-types:
None
Name
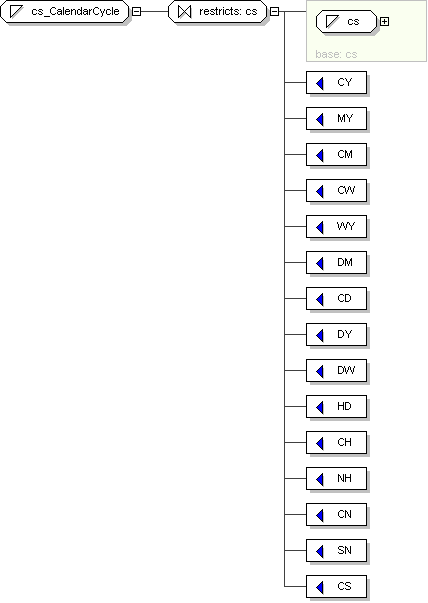
cs_CalendarCycle
Content
value comes from list: {'CY'|'MY'|'CM'|'CW'|'WY'|'DM'|'CD'|'DY'|'DW'|'HD'|'CH'|'NH'|'CN'|'SN'|'CS'}
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:simpleType
name ="
cs_CalendarCycle ">
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
cs
">
<xsd:enumeration
value ="CY "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="MY "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="CM "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="CW "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="WY "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="DM "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="CD "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="DY "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="DW "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="HD "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="CH "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="NH "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="CN "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="SN "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="CS "/>
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:simpleType >
Super-types:
xsd :token <
cs
(by restriction) < cs_CompressionAlgorithm (by restriction)
Sub-types:
None
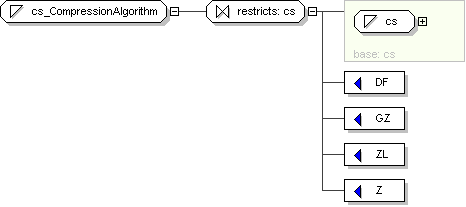
Name
cs_CompressionAlgorithm
Content
value comes from list: {'DF'|'GZ'|'ZL'|'Z'}
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:simpleType
name ="
cs_CompressionAlgorithm ">
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
cs
">
<xsd:enumeration
value ="DF "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="GZ "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="ZL "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="Z "/>
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:simpleType >
Super-types:
xsd :token <
cs
(by restriction) < cs_EntityNamePartQualifier (by restriction)
Sub-types:
None
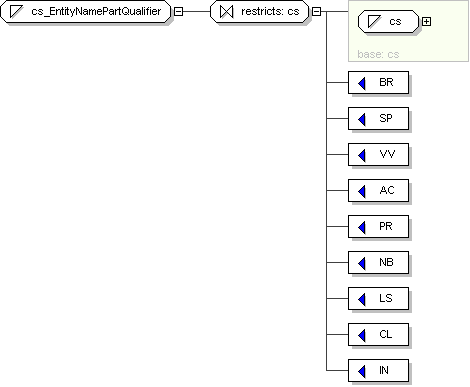
Name
cs_EntityNamePartQualifier
Content
value comes from list: {'BR'|'SP'|'VV'|'AC'|'PR'|'NB'|'LS'|'CL'|'IN'}
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:simpleType
name ="
cs_EntityNamePartQualifier ">
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
cs
">
<xsd:enumeration
value ="BR "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="SP "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="VV "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="AC "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="PR "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="NB "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="LS "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="CL "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="IN "/>
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:simpleType >
Super-types:
xsd :token <
cs
(by restriction) < cs_EntityNamePartType (by restriction)
Sub-types:
None
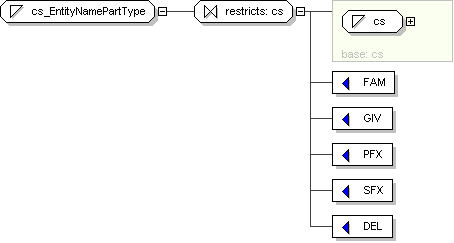
Name
cs_EntityNamePartType
Content
value comes from list: {'FAM'|'GIV'|'PFX'|'SFX'|'DEL'}
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:simpleType
name ="
cs_EntityNamePartType ">
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
cs
">
<xsd:enumeration
value ="FAM "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="GIV "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="PFX "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="SFX "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="DEL "/>
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:simpleType >
Super-types:
xsd :token <
cs
(by restriction) < cs_EntityNameUse (by restriction)
Sub-types:
None
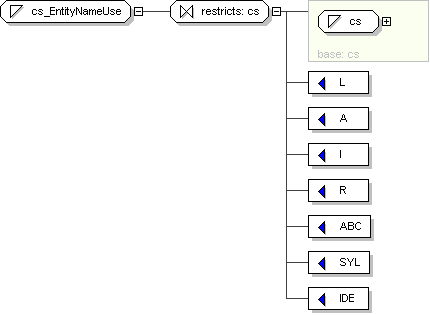
Name
cs_EntityNameUse
Content
value comes from list: {'L'|'A'|'I'|'R'|'ABC'|'SYL'|'IDE'}
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:simpleType
name ="
cs_EntityNameUse ">
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
cs
">
<xsd:enumeration
value ="L "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="A "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="I "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="R "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="ABC "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="SYL "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="IDE "/>
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:simpleType >
Super-types:
xsd :token <
cs
(by restriction) < cs_IntegrityCheckAlgorithm (by restriction)
Sub-types:
None
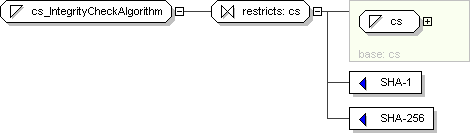
Name
cs_IntegrityCheckAlgorithm
Content
value comes from list: {'SHA-1'|'SHA-256'}
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:simpleType
name ="
cs_IntegrityCheckAlgorithm ">
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
cs
">
<xsd:enumeration
value ="SHA-1 "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="SHA-256 "/>
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:simpleType >
Super-types:
xsd :token <
cs
(by restriction) < cs_NullFlavor (by restriction)
Sub-types:
None
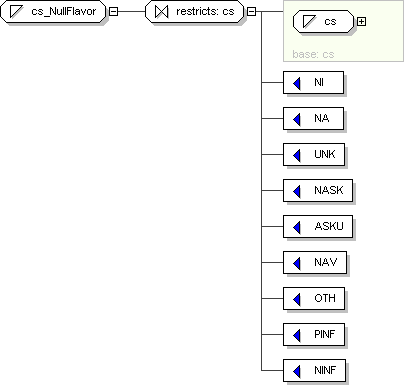
Name
cs_NullFlavor
Content
value comes from list: {'NI'|'NA'|'UNK'|'NASK'|'ASKU'|'NAV'|'OTH'|'PINF'|'NINF'}
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:simpleType
name ="
cs_NullFlavor ">
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
cs
">
<xsd:enumeration
value ="NI "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="NA "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="UNK "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="NASK "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="ASKU "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="NAV "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="OTH "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="PINF "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="NINF "/>
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:simpleType >
Super-types:
xsd :token <
cs
(by restriction) < cs_PostalAddressUse (by restriction)
Sub-types:
None
Name
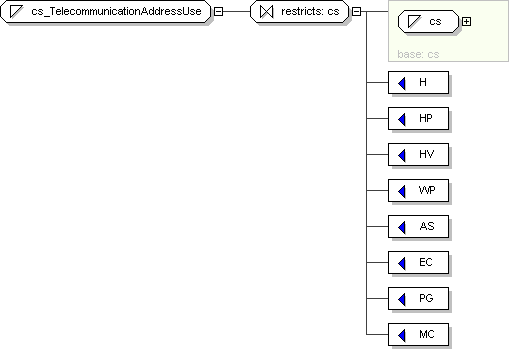
cs_PostalAddressUse
Content
value comes from list: {'PHYS'|'PST'|'TMP'|'BAD'|'H'|'HP'|'HV'|'WP'|'ABC'|'SYL'|'IDE'}
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:simpleType
name ="
cs_PostalAddressUse ">
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
cs
">
<xsd:enumeration
value ="PHYS "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="PST "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="TMP "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="BAD "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="H "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="HP "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="HV "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="WP "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="ABC "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="SYL "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="IDE "/>
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:simpleType >
Super-types:
xsd :token <
cs
(by restriction) < cs_ProbabilityDistributionType (by restriction)
Sub-types:
None
Name
cs_ProbabilityDistributionType
Content
value comes from list: {'U'|'N'|'LN'|'G'|'E'|'X2'|'T'|'F'|'B'}
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:simpleType
name ="
cs_ProbabilityDistributionType ">
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
cs
">
<xsd:enumeration
value ="U "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="N "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="LN "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="G "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="E "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="X2 "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="T "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="F "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="B "/>
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:simpleType >
Super-types:
xsd :token <
cs
(by restriction) < cs_SetOperator (by restriction)
Sub-types:
None
Name
cs_SetOperator
Content
value comes from list: {'I'|'E'|'A'|'H'|'P'}
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:simpleType
name ="
cs_SetOperator ">
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
cs
">
<xsd:enumeration
value ="I "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="E "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="A "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="H "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="P "/>
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:simpleType >
Super-types:
xsd :token <
cs
(by restriction) < cs_TelecommunicationAddressUse (by restriction)
Sub-types:
None
Name
cs_TelecommunicationAddressUse
Content
value comes from list: {'H'|'HP'|'HV'|'WP'|'AS'|'EC'|'PG'|'MC'}
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:simpleType
name ="
cs_TelecommunicationAddressUse ">
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
cs
">
<xsd:enumeration
value ="H "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="HP "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="HV "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="WP "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="AS "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="EC "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="PG "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="MC "/>
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:simpleType >
Super-types:
xsd :token <
cs
(by restriction) < cs_TimingEvent (by restriction)
Sub-types:
None
Name
cs_TimingEvent
Content
value comes from list: {'AC'|'ACD'|'ACM'|'ACV'|'HS'|'IC'|'ICD'|'ICM'|'ICV'|'PC'|'PCD'|'PCM'|'PCV'}
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:simpleType
name ="
cs_TimingEvent ">
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
cs
">
<xsd:enumeration
value ="AC "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="ACD "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="ACM "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="ACV "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="HS "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="IC "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="ICD "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="ICM "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="ICV "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="PC "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="PCD "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="PCM "/>
<xsd:enumeration
value ="PCV "/>
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:simpleType >
Simple Type: int
Super-types:
xsd :integer < int (by restriction)
Sub-types:
None
Name
int
Content
Documentation
Integer numbers (-1,0,1,2, 100, 3398129, etc.) are precise numbers
that are results of counting and enumerating. Integer numbers are
discrete, the set of integers is infinite but countable. No arbitrary
limit is imposed on the range of integer numbers. Two NULL flavors are
defined for the positive and negative infinity.
Application Data
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:simpleType
name ="
int ">
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
xsd :integer
"/>
</
xsd:simpleType >
Simple Type: oid
Super-types:
xsd :string < oid (by restriction)
Sub-types:
None
Name
oid
Content
pattern = ([1-9][0-9]*)(\.[1-9][0-9]*)*
Documentation
Application Data
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:simpleType
name ="
oid ">
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
xsd :string
">
<xsd:pattern
value ="([1-9][0-9]*)(\.[1-9][0-9]*)* "/>
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:simpleType >
Simple Type: real
Super-types:
None
Sub-types:
None
Name
real
Content
Union of following types:
Documentation
Fractional numbers. Typically used whenever quantities are measured,
estimated, or computed from other real numbers. The typical
representation is decimal, where the number of significant decimal
digits is known as the precision.
Real numbers are needed beyond integers whenever quantities of the
real world are measured, estimated, or computed from other real
numbers. The term "Real number" in this specification is used to mean
that fractional values are covered without necessarily implying the
full set of the mathematical real numbers.
Application Data
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:simpleType
name ="
real ">
<
xsd:union
memberTypes ="
xsd :decimal xsd :double "/>
</
xsd:simpleType >
Simple Type: ruid
Super-types:
xsd :string < ruid (by restriction)
Sub-types:
None
Name
ruid
Content
pattern = [A-Za-z][A-Za-z0-9\-]*
Documentation
Application Data
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:simpleType
name ="
ruid ">
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
xsd :string
">
<xsd:pattern
value ="[A-Za-z][A-Za-z0-9\-]* "/>
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:simpleType >
Super-types:
None
Sub-types:
None
Name
set_cs_EntityNamePartQualifier
Content
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:simpleType
name ="
set_cs_EntityNamePartQualifier ">
</
xsd:simpleType >
Super-types:
None
Sub-types:
None
Name
set_cs_EntityNameUse
Content
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:simpleType
name ="
set_cs_EntityNameUse ">
</
xsd:simpleType >
Super-types:
None
Sub-types:
None
Name
set_cs_PostalAddressUse
Content
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:simpleType
name ="
set_cs_PostalAddressUse ">
</
xsd:simpleType >
Super-types:
None
Sub-types:
None
Name
set_cs_TelecommunicationAddressUse
Content
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:simpleType
name ="
set_cs_TelecommunicationAddressUse ">
</
xsd:simpleType >
Simple Type: st
Super-types:
xsd :string < st (by restriction)
Sub-types:
None
Name
st
Content
Documentation
The character string data type stands for text data, primarily
intended for machine processing (e.g., sorting, querying, indexing,
etc.) Used for names, symbols, and formal expressions.
Application Data
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:simpleType
name ="
st ">
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
xsd :string
">
<xsd:minLength
value ="1 "/>
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:simpleType >
Simple Type: ts
Super-types:
xsd :string < ts (by restriction)
Sub-types:
None
Name
ts
Content
pattern = [0-9]{1,8}|([0-9]{9,14}|[0-9]{14,14}\.[0-9]+)([+\-][0-9]{1,4})?
Documentation
A quantity specifying a point on the axis of natural time. A point
in time is most often represented as a calendar expression.
Application Data
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:simpleType
name ="
ts ">
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
xsd :string
">
<xsd:pattern
value ="[0-9]{1,8}|([0-9]{9,14}|[0-9]{14,14}\.[0-9]+)([+\-][0-9]{1,4})? "/>
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:simpleType >
Simple Type: uid
Super-types:
None
Sub-types:
None
Name
uid
Content
Union of following types:
Documentation
Application Data
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:simpleType
name ="
uid ">
</
xsd:simpleType >
Simple Type: url
Super-types:
xsd :anyURI < url (by restriction)
Sub-types:
None
Name
url
Content
Documentation
A telecommunications address specified according to Internet standard
RFC 1738 [http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc1738.txt]. The
URL specifies the protocol and the contact point defined by that
protocol for the resource. Notable uses of the telecommunication
address data type are for telephone and telefax numbers, e-mail
addresses, Hypertext references, FTP references, etc.
Application Data
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:simpleType
name ="
url ">
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
xsd :anyURI
"/>
</
xsd:simpleType >
Simple Type: uuid
Super-types:
xsd :string < uuid (by restriction)
Sub-types:
None
Name
uuid
Content
pattern = [0-9a-zA-Z]{8}-[0-9a-zA-Z]{4}-[0-9a-zA-Z]{4}-[0-9a-zA-Z]{4}-[0-9a-zA-Z]{12}
Documentation
Application Data
Schema Component Representation
<
xsd:simpleType
name ="
uuid ">
<
xsd:restriction
base ="
xsd :string
">
<xsd:pattern
value ="[0-9a-zA-Z]{8}-[0-9a-zA-Z]{4}-[0-9a-zA-Z]{4}-[0-9a-zA-Z]{4}-[0-9a-zA-Z]{12} "/>
</
xsd:restriction >
</
xsd:simpleType >
Complex Type:
Schema Component Type
AusAddress
Schema Component Name
Super-types:
Address < AusAddress (by extension)
Sub-types:
QLDAddress (by restriction)
If this schema component is a type definition, its type hierarchy is shown in a gray-bordered box.
The table above displays the properties of this schema component.
XML Instance Representation
<...
country="Australia "
>
<unitNo> string </unitNo> [0..1]
<houseNo> string </houseNo> [1]
<street> string </street> [1]
Start Choice
[1]
<city> string </city> [1]
<town> string </town> [1]
End Choice
<state> AusStates </state> [1]
<postcode> string <<pattern = [1-9][0-9]{3}>> </postcode> [1]
?
</...>
The XML Instance Representation table above shows the schema component's content as an XML instance.
The minimum and maximum occurrence of elements and attributes are provided in square brackets, e.g. [0..1].
Model group information are shown in gray, e.g. Start Choice ... End Choice.
For type derivations, the elements and attributes that have been added to or changed from the base type's content are shown in bold .
If an element/attribute has a fixed value, the fixed value is shown in green, e.g. country="Australia".
Otherwise, the type of the element/attribute is displayed.
If the element/attribute's type is in the schema, a link is provided to it.
For local simple type definitions, the constraints are displayed in angle brackets, e.g. <<pattern = [1-9][0-9]{3}>>.
If a local element/attribute has documentation, it will be displayed in a window that pops up when the question mark inside the attribute or next to the element is clicked, e.g. <postcode>.
Schema Component Representation
<complexType
name ="AusAddress ">
<complexContent >
<extension
base ="
Address
">
<sequence >
<element
name ="state " type ="
AusStates
"/>
<element
name ="postcode ">
<simpleType >
<restriction
base ="
string
">
<pattern
value ="[1-9][0-9]{3} "/>
</restriction >
</simpleType >
</element >
</sequence >
<attribute
name ="country " type ="
string
" fixed ="Australia "/>
</extension >
</complexContent >
</complexType >
The Schema Component Representation table above displays the underlying XML representation of the schema component. (Annotations are not shown.)
Abstract
(Applies to complex type definitions and element declarations). An abstract element or complex type cannot used to validate an element instance. If there is a reference to an abstract element, only element declarations that can substitute the abstract element can be used to validate the instance. For references to abstract type definitions, only derived types can be used.
All Model Group
Child elements can be provided in any order in instances. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#element-all .
Choice Model Group
Only one from the list of child elements and model groups can be provided in instances. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#element-choice .
Collapse Whitespace Policy
Replace tab, line feed, and carriage return characters with space character (Unicode character 32). Then, collapse contiguous sequences of space characters into single space character, and remove leading and trailing space characters.
Disallowed Substitutions
(Applies to element declarations). If substitution is specified, then substitution group members cannot be used in place of the given element declaration to validate element instances. If derivation methods , e.g. extension, restriction, are specified, then the given element declaration will not validate element instances that have types derived from the element declaration's type using the specified derivation methods. Normally, element instances can override their declaration's type by specifying an xsi:type attribute.
Key Constraint
Like Uniqueness Constraint , but additionally requires that the specified value(s) must be provided. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#cIdentity-constraint_Definitions .
Key Reference Constraint
Ensures that the specified value(s) must match value(s) from a Key Constraint or Uniqueness Constraint . See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#cIdentity-constraint_Definitions .
Model Group
Groups together element content, specifying the order in which the element content can occur and the number of times the group of element content may be repeated. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#Model_Groups .
Nillable
(Applies to element declarations). If an element declaration is nillable, instances can use the xsi:nil attribute. The xsi:nil attribute is the boolean attribute, nil , from the http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance namespace. If an element instance has an xsi:nil attribute set to true, it can be left empty, even though its element declaration may have required content.
Notation
A notation is used to identify the format of a piece of data. Values of elements and attributes that are of type, NOTATION, must come from the names of declared notations. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#cNotation_Declarations .
Preserve Whitespace Policy
Preserve whitespaces exactly as they appear in instances.
Prohibited Derivations
(Applies to type definitions). Derivation methods that cannot be used to create sub-types from a given type definition.
Prohibited Substitutions
(Applies to complex type definitions). Prevents sub-types that have been derived using the specified derivation methods from validating element instances in place of the given type definition.
Replace Whitespace Policy
Replace tab, line feed, and carriage return characters with space character (Unicode character 32).
Sequence Model Group
Child elements and model groups must be provided in the specified order in instances. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#element-sequence .
Substitution Group
Elements that are members of a substitution group can be used wherever the head element of the substitution group is referenced.
Substitution Group Exclusions
(Applies to element declarations). Prohibits element declarations from nominating themselves as being able to substitute a given element declaration, if they have types that are derived from the original element's type using the specified derivation methods.
Target Namespace
The target namespace identifies the namespace that components in this schema belongs to. If no target namespace is provided, then the schema components do not belong to any namespace.
Uniqueness Constraint
Ensures uniqueness of an element/attribute value, or a combination of values, within a specified scope. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#cIdentity-constraint_Definitions .